Queries
For most work, I use entityQueries. There are a few circumstances where I've needed to get into the SQL which meant using static or dynamic queries. There are examples of these different techniques below.
entityQuery
Find matching nodes entityQuery
In this entityQuery example, we search for nodes of content type (or bundle) ws_product and match field_product_sku with the $sku variable.
use Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
function getProductId($sku) {
$productId = false;
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'ws_product')
->condition('field_product_sku', $sku)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
if ($nids) {
$nid = array_values($nids);
$node = Node::load($nid[0]);
$productId = $node->get('field_product_id')->value;
}
return $productId;
}Find matching nodes entityQuery
In this entityQuery, we search for published nodes of type contract with field_contract_status having the value "Active". This puts the resulting nids and node titles in a render array for display.
This is a simple query which outputs a bunch of nids and titles
public function loadRawSalesforceData() {
$node_storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'contract')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('field_contract_status', 'Active')
->sort('title', 'DESC')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
if ($nids) {
$nodes = $node_storage->loadMultiple($nids);
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$nid = $node->id();
$titles[] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => "<p>" . "nid=$nid " . "Title=" . $node->getTitle(). "</p>",
];
}
return $titles;
}
return [
'#markup' => $this->t('nothing, nada, not a sausage'),
];
}Find matching article nodes entityQuery
This example looks for an entity of type article with the name $name
public function entityExists() {
$name = 'hello';
// See if the article named hello exists.
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'article')
->condition('title', $name)
->count()
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$count_nodes = $query->execute();
if ($count_nodes == 0) {
$str = "Found no articles";
}
elseif ($count_nodes > 0) {
$str = "Found $count_nodes articles";
}
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}Find nodes that match a taxonomy term entityQuery
Find all nodes that match a term_id and retrieve the first 5 nodes sorted by title. This code also puts them into a render array for display.
protected function loadFirstOpinion($term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->sort('title', 'ASC') //or DESC
->range(0, 5)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
$nodes = $storage->loadMultiple($nids);
$render_array = [];
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$render_array[] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => '<p>' . $node->getTitle(),
];
}
return $render_array;Find 5 nodes that have a matching taxonomy term
Look for published nodes of node type opinion that have a term in the category field, sorted by title ascending, starting with the first result and returning 5 results. The resulting titles are put into a render array.
protected function loadFirstOpinion($term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->sort('title', 'ASC') //or DESC
->range(0, 5)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
$nodes = $storage->loadMultiple($nids);
$render_array = [];
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$render_array[] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => '<p>' . $node->getTitle(),
];
}
return $render_array;Find matching nodes and delete them
Use an entityQuery to find the first 10 nodes of type event and delete them. Return a render array with a message for display.
public function deleteQuery1() {
$results = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'event')
->range(0, 10)
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->execute();
if ($results) {
foreach ($results as $result) {
$node = Node::load($result);
$node->delete();
}
}
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => t("10 nodes deleted."),
];
return $render_array;
}Sort by Node ID(nid) or title
// Descending.
$query->sort('nid', 'DESC');
// Or ascending.
$query->sort('nid', 'ASC');
// Or node title.
$query->sort('title', 'ASC');Slice up entityQuery results into batches of 100 nodes
This is often used for batch API operations.
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'contract')
->condition('status', 1)
->sort('title', 'ASC')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
$nid_count = count($nids);
// Grab 100 nids at a time to batch process.
$batches = [];
for ($i=0;$i<=$nid_count;$i+=100) {
$batches[] = array_slice($nids, $i, 100);
}Query the creation date (among other things) using entityQuery
Note, the created (and changed) field uses a Unix timestamp. This is an int 11 field in the db with a value like 1525302749. If you add a Drupal datefield, its data looks like 2019-05-15T21:32:00 (varchar 20)
If you want to query a date field in a content type, you will have to fiddle around with the setTimezone stuff that is commented out below. The date field referenced below (field_date) is a standard Drupal date field.
protected function loadOpinionForAYear($year, $term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
// Get a date string suitable for use with entity query.
// $date = new DrupalDateTime(); // now
$format = 'Y-m-d H:i';
$start_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat($format, $year . "-01-01 00:00");
$end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat($format, $year . "-12-31 23:59");
$start_date = $start_date->getTimestamp();
$end_date = $end_date->getTimestamp();
// $start_date->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone(DateTimeItemInterface::STORAGE_TIMEZONE));
// $end_date->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone(DateTimeItemInterface::STORAGE_TIMEZONE));
// $start_date = $start_date->format(DateTimeItemInterface::DATETIME_STORAGE_FORMAT);
// $end_date = $end_date->format(DateTimeItemInterface::DATETIME_STORAGE_FORMAT);
// Set the condition.
// $query->condition('field_date.value', $start_date, '>=');
// $query->condition('field_date.value', $end_date, '<=');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->condition('created', $start_date, '>=')
->condition('created', $end_date, '<=')
->sort('title', 'DESC')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
$titles = [];
if ($nids) {
$nodes = $storage->loadMultiple($nids);
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$titles[]= $node->getTitle();
}
}
return $titles;
}More at this 2018 blog post and on Stack Exchange
Frequently used conditions for entityQuery
- Published:
->condition('status', 1) - Text field not empty:
->condition('field_source_url', '', '<>') - Field value > 14:
->condition('field_some_field', 14, '>') - Reference field empty:
->notExists('field_sf_account_ref'); - Null:
->condition($field, NULL, 'IS NULL'); - Not Null:
->condition($field,NULL, 'IS NOT NULL');
More conditions on Drupal.org updated Aug 2024
Menu query to update menu items programmatically
To update several items in a menu, you could use hook_update.
function park_academy_update_8002() {
$mids = \Drupal::entityQuery('menu_link_content')
->condition('menu_name', 'park-wide-utility')
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->execute();
foreach($mids as $mid) {
$menu_link = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('menu_link_content')->load($mid);
$title = $menu_link->getTitle();
if ($title === 'Support') {
$menu_link->set('weight',2);
$menu_link->set('expanded', TRUE);
// $menu_link->set('title','yomama');
$menu_link->set('link', 'https://www.google.com');
$menu_link->save();
}
}
}Query multi-value fields
When querying multivalue fields, you can specify the %delta to identify the position (or delta) for the value you are looking for. In the example below, we specify field_srp_voting_status.%delta as 1 to indicate the second position (it is zero-based). We use field_srp_voting_status.%delta.value for the actual value we are looking for (either accepted, rejected or incomplete):
// Find correlation nodes with accepted, rejected or incomplete in the
// $field_voting_status in position 1.
$vote_number = 1;
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'correlation', '=')
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->condition('field_program', $this->programNid, '=')
->condition('field_voting_status.%delta', $vote_number, '=')
->condition('field_voting_status.%delta.value', [
'accepted',
'rejected',
'incomplete'
], 'IN')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$correlation_nids = $query->execute();
$correlation_nids = array_values($correlation_nids);
return $correlation_nids;Match entity reference fields that have values or don't
Use the following to check if there is a value in an entity reference field:
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'srp_voting_record')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
if ($vote_type == 'citation') {
// Check for empty entity reference field.
$query->notExists('field_ref_error_feedback');
}
if ($vote_type == 'feedback_error'){
// Check for filled entity reference field.
$query->exists('field_ref_error_feedback');
}Query a field in the entity in entity reference fields
To find a matching user id in the entity (user) that is referenced in the entity reference field field_voter, you can query the field_voter.entity:user.uid value:
protected function loadErrorFeedbackVotingRecordNode(int $user_id, int $error_feedback_nid, int $vote_number) {
$node = [];
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'stp_voting_record')
->condition('field_voter.entity:user.uid', $user_id)
->condition('field_ref_error_feedback', $error_feedback_nid)
->condition('field_srp_vote_number', $vote_number)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
if (!empty($nids)) {
$nid = reset($nids);
$node = Node::load($nid);
}
return $node;
}This syntax lets you look at any entity that is referenced in an entity reference field and search for a field value in that entity. E.g., you can look in field_first_name for the value Fred:
->condition('field_tts_pub_expectation.entity.field_first_name', 'Fred', '=')Find values in multi-value entity reference fields
To match a single value, use IN or NOT IN as the operator.
This will find any nodes with tid 2 in the taxonomy entity reference field:
$tid = 2;
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', NODE_PUBLISHED)
->condition('type', 'custom_type')
->condition('field_category', $tid, 'IN')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
->sort('field_last_name', DESC);This will find nodes with 2 or 8 in the taxonomy entity reference field:
$tids = [2,8];
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', NODE_PUBLISHED)
->condition('type', 'custom_type')
->condition('field_category', $tids, 'IN')
->accessCheck(FALSE);
->sort('field_last_name', DESC);Find multiple values in a multi-value entity reference field
For an exact match to an array, use andConditionGroup
Use two separate andConditionGroup(). This will find nodes with a tid match of both 2 and 8:
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', NODE_PUBLISHED)
->condition('type', 'custom_type');
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$and = $query->andConditionGroup();
$and->condition('field_category', 2);
$query->condition($and);
$and = $query->andConditionGroup();
$and->condition('field_category', 8);
$query->condition($and);
$result = $query->execute();This works no matter how many terms are in the field or in which delta they are.
For a dynamic array, put this in a foreach loop:
// An array to match. someFunc is your custom code that returns an array
$dynamic_array = someFunc();
// Start the query.
$custom_query = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('node')
->getQuery();
// Set the parameters. Could be multiple so use `andConditionGroup`.
if (!empty($dynamic_array)) {
foreach ($dynamic_array as $value_integer) {
$and = $custom_query->andConditionGroup();
$and->condition('field_my_multivalue_ref', $value_integer, 'IN');
$custom_query->condition($and);
}
}
else {
$custom_query->condition('field_my_multivalue_ref', NULL, 'IS NULL');
}
$custom_query
->accessCheck(FALSE)
// any other conditions you want to add, like:
->condition('type', 'my_node_type');
$result = $custom_query->execute();Find nodes that were modified recently
To select for nodes that were modified within the last seven days, use the following:
$num_days_string = '-7 days';
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'srp_voting_record')
->condition('changed', strtotime($num_days_string), '>=');
->accessCheck(FALSE)
$voting_record_nids = $query->execute();
if (empty($voting_record_nids)) {
return [];
}
// Re-arrange indexing as 0, 1, 2...
$voting_record_nids = array_values($voting_record_nids);andCondition and orCondition example
Here is an example of a submitForm function which deletes the node then queries for nodes that are either:
- Of type
srp_voting_recordswith matching$ef_node_id - Of type
srp_publisher_responsewith matching$ef_node_idThen it deletes those nodes it found.
Note, the ef in $ef_node_id stands for error/feedback if that makes the code any clearer.
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$ef_node_id = $form_state->get('ef_node_id');
$program_nid = $form_state->get('program_nid');
$type_text = $form_state->get('type_text');
$node = Node::load($ef_node_id);
if($node) {
$node->delete();
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage("{$type_text} deleted.");
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->sort('title', 'ASC');
$orCorr1 = $query->andConditionGroup()
->condition('type', 'srp_voting_record', '=')
->condition('field_ref_error_feedback', $ef_node_id, '=');
$orCorr2 = $query->andConditionGroup()
->condition('type', 'srp_publisher_response', '=')
->condition('field_srp_feedback_error_item', $ef_node_id, '=');
$orCorr3 = $query->orConditionGroup()
->condition($orCorr1)
->condition($orCorr2);
$query->condition($orCorr3);
$nids = $query->execute();
foreach($nids as $nid)
{
$delete_node = Node::load($nid);
$delete_node->delete();
}
}
else {
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage("{$type_text} Not Found.");
}
$referrer_alias = $form_state->get("referrer_alias");
$url = Url::fromUri('internal:' . $referrer_alias);
$form_state->setRedirectUrl($url);
}More details about condition
from - API documentation for QueryInterface::condition
Language-specific query
This example shows searching for entities with both the Turkish 'merhaba' (notice 'tr' as the last parameter) and the Polish 'siema' (notice 'pl' as the last parameter) within a 'greetings' text field:
$entity_ids = \Drupal::entityQuery($entity_type)
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->condition('greetings', 'merhaba', '=', 'tr')
->condition('greetings.value', 'siema', '=', 'pl')
->execute();Parameters
Notice that the first parameter can be a string or a ConditionInterface:
string|\Drupal\Core\Entity\Query\ConditionInterface $field: Name of the field being queried or an instance of ConditionInterface. In the case of the name, it must contain a field name, optionally followed by a column name. The column can be the reference property, usually "entity", for reference fields and that can be followed similarly by a field name and so on. Additionally, the target entity type can be specified by appending the ":target_entity_type_id" to "entity". Some examples:
- nid
- tags.value
- tags
- tags.entity.name
- tags.entity:taxonomy_term.name
- uid.entity.name
- uid.entity:user.name
"tags" is the same as "tags.value" as value is the default column. If two or more conditions have the same field names they apply to the same delta within that field. In order to limit the condition to a specific item a numeric delta should be added between the field name and the column name.
->condition('tags.5.value', 'news')This will require condition to be satisfied on a specific delta of the field. The condition above will require the 6th value of the field to match the provided value. Further, it's possible to create a condition on the delta itself by using '%delta'. For example,
->condition('tags.%delta', 5)will find only entities which have at least six tags. Finally, the condition on the delta itself, accompanied by a condition on the value, will require the value to appear in the specific delta range. For example,
->condition('tags.%delta', 0, '>'))
->condition('tags.%delta.value', 'news'))will only find the "news" tag if it is not the first value. It should be noted that conditions on specific deltas and delta ranges are only supported when querying content entities.
string|int|bool|array|null $value: (optional) The value for $field. In most cases, this is a scalar and it's treated as case-insensitive. For more complex operators, it is an array. The meaning of each element in the array is dependent on $operator. Defaults to NULL, for most operators (except: 'IS NULL', 'IS NOT NULL') it always makes the condition false.
string|null $operator: (optional) The comparison operator. Possible values: '=', '<>', '>', '>=', '<', '<=', 'STARTS_WITH', 'CONTAINS', 'ENDS_WITH': These operators expect $value to be a literal of the same type as the column. 'IN', 'NOT IN': These operators expect $value to be an array of literals of the same type as the column. 'IS NULL', 'IS NOT NULL': These operators ignore $value, for that reason it is recommended to use a $value of NULL for clarity. 'BETWEEN', 'NOT BETWEEN': These operators expect $value to be an array of two literals of the same type as the column. If NULL, defaults to the '=' operator.
string|null $langcode: (optional) The language code allows filtering results by specific language. If two or more conditions omit the langcode within one condition group, then they are presumed to apply to the same translation. If within one condition group one condition has a langcode and another does not, they are not presumed to apply to the same translation. If omitted (NULL), any translation satisfies the condition.
User Query example
/**
* Get the active publisher admins and editors for this publisher nid.
*
* @param int $publisher_nid
* The publisher nid.
* @param array $roles
* The roles to check for.
*
* @return array
* The active publisher admins and editors for this publisher nid.
*/
public static function getActivePublisherUsers(int $publisher_nid, array $roles = ['publisher_edit', 'publisher', 'publisher_staff', 'publisher_view']): array {
$uids = \Drupal::entityQuery('user')
->condition('field_teks_publisher', $publisher_nid)
// ->condition('roles.target_id', ['publisher_edit', 'publisher'], 'IN')
->condition('roles', ['publisher_edit', 'publisher'], 'IN')
->condition('status', 1)
->sort('created', 'ASC')
->accessCheck(FALSE)
->execute();
$publisher_editors = [];
foreach ($uids as $uid) {
$user = User::load($uid);
$publisher_editors[] = [
'uid' => $uid,
'name' => $user->getAccountName(),
'email' => $user->getEmail(),
];
}
return $publisher_editors;
}Paragraph entityQuery example
This code looks up related paragraphs of type accordio_video_section, grabs the first one (this should have used a sort to more reliably return the same value), then finds all video_collection nodes in that collection. In summary, this finds a list of other videos that are in the collection for the video you are viewing. Think of it as a related video list.
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state, $nojs = NULL) {
...
// Grab nid of the current video detail node.
$nid = 0;
$nodeTitle = '';
$default = '';
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
$nid = $node->id();
$nodeType = $node->bundle();
$nodeTitle = $node->getTitle();
// Default value for select element.
$default = '/node/' . $nid;
}
$form['title'] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => $nodeTitle,
];
// Find a paragraph that has the node I am currently viewing.
$paragraph_id = 0;
$storage = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('paragraph');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('paragraph')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'accordio_video_section')
->condition('field_content_relation', $nid)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$ids = $query->execute();
if (!$ids) {
return;
}
$paragraphs = $storage->loadMultiple($ids);
if ($paragraphs) {
// Grab the first one.
$paragraph_id = reset($paragraphs)->id();
}
// Find the video collection node that has this paragraph.
$nids = [];
$video_collection_title = '';
if ($paragraph_id) {
$storage = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'video_collection')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('field_video_accordions', $paragraph_id)
->accessCheck(FALSE);
$nids = $query->execute();
}
if ($nids) {
$video_collection_nid = reset($nids);
$video_collection_node = Node::load($video_collection_nid);
$video_collection_title = $video_collection_node->label();
}
$form['collection_title'] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => $video_collection_title,
];
// Now go find all the videos in this video_collection.
$videos = [];
$storage = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('paragraph');
// Grab all the accordions and extract out the videos.
if (isset($video_collection_node)) {
$accordions = $video_collection_node->get('field_video_accordions');
foreach ($accordions as $accordion) {
if ($accordion->entity->getType() == 'accordio_video_section') {
$id = $accordion->target_id;
$accordion_paragraph = $storage->load($id);
$accordion_videos = reset($accordion_paragraph->field_content_relation);
$videos = array_merge($videos, $accordion_videos);
}
}
}Static and Dynamic Queries
Sometimes you will use static or dynamic queries rather than entityQueries. These use actual SQL versus the entityQuery approach, where you build the various parts of the query using PHP methods. I have seen a situation where a static query would work, where an entityQuery would not.
Note
Dynamic queries let the Drupal database driver generate the SQL string and therefore have more flexibility in the resulting SQL string. Static queries are just a SQL string which have no flexibility in making small adjustments for a specific database back-end. This may not work for other databases. The core supported databases are MySQL, PostgreSQL and SQLite. Dynamic queries should work for more/all databases. Dynamic queries are, however, a little bit slower than static queries.
An example static query is:
$database = \Drupal::database();
$query = $database->query("SELECT id, example FROM {mytable}");
$result = $query->fetchAll();Dynamic queries refer to queries that are built dynamically by Drupal rather than provided as an explicit query string. All insert, update, delete, and merge queries must be dynamic. Select queries may be either static or dynamic. Therefore, "dynamic query" generally refers to a dynamic select query.
For this static query:
$result = $database
->query("SELECT uid, name, status, created, access
FROM {users_field_data} u
WHERE uid <> 0
LIMIT 50
OFFSET 0"
);The equivalent dynamic query is:
// Create a Select object and directly add extra details
// like a condition, fields and a range.
$query = $database->select('users_field_data', 'u')
->condition('u.uid', 0, '<>')
->fields('u', ['uid', 'name', 'status', 'created', 'access'])
->range(0, 50);For more info, check out
Get a connection object
There are two ways to get a connection object:
/** @var \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection $connection */
$connection = Database::getConnection();
//OR
/** @var \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection $connection */
$connection = \Drupal::service('database');SQL select examples
Here is a static query example from a controller. This loads some fields from the donors table and returns a render array with a count of how many results it found.
public function queryBuild1() {
$database = \Drupal::database();
$query = $database->query("SELECT id, name, amount FROM {donors}");
$results = $query->fetchAll();
$result_count = count($results);
$str = "Results from db query";
$str .= "<br/> Result count = $result_count";
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}Another example which loads all the nodes of type page and returns the node id and title.
use Drupal\Core\Database\Connection;
public function queryBuild2() {
$connection = \Drupal::database();
$query = $connection->select('node', 'n');
$query->fields('n', ['nid']);
$query->condition('n.type', 'page');
$results = $query->execute();
foreach ($results as $row) {
$node = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node')->load($row->nid);
if ($node) {
$nid = $node->id();
$title = $node->getTitle();
//...
}
...
}
}Find the biggest value in a field
Here is a query to find the highest value for the id column in the donors table.
public function highestId() {
$database = \Drupal::database();
$connection = Database::getConnection();
$query = $connection->select('donors', 'n');
$query->addExpression('MAX(id)', 'id');
$result = $query->execute();
$highest_id = intval($result->fetchField());
$str = "Highest id = $highest_id";
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}SQL update query - example 1
This code finds records which have matching uuid, have a status of new and the event is either update or add. It then updates the status to the value passed in the $status parameter.
public function setUpdateStatus(string $uuid, string $status) {
$db_connection = \Drupal::database();
$result = $db_connection->update('nocs_info')
->fields(['status' => $status])
->condition('uuid', $uuid)
->condition('event', ['UPDATE', 'ADD'], 'IN')
->condition('status', 'new')
->execute();
return $result;
}SQL update query - example 2
/**
* Converts imported eventlog item/s from UPDATE to ADD by uuid.
*
* @param string $uuid
* UUID for events to convert from UPDATE to ADD.
*
* @return mixed
* Results of update query.
*/
public function convertUpdateToAddEvent(string $uuid) {
$update_connection = \Drupal::database();
$result = $update_connection->update('nocs_connect')
->fields([
'event' => 'ADD',
])
->condition('uuid', $uuid)
->condition('event', 'UPDATE')
->condition('status', 'new')
->execute();
return $result;
}SQL update query - example 3
This will update values in a table and return the number of rows updated.
//use Drupal\Core\Database\Database;
public function updateQuery1() {
$database = \Drupal::database();
$query_string = "Update {donors} set amount=amount+1 where id<=10 ";
$affectedRows = $database->query($query_string,[],
['return' => Database::RETURN_AFFECTED]);
$str = "Affected rows = $affectedRows";
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}Note
This will return the number of rows affected by the SQL update query although this RETURN_AFFECTED functionality will be deprecated in Drupal version 11. See rowCount for Drupal 9 and Drupal 10 source code.
// Depending on the type of query we may need to return a different value.
// See DatabaseConnection::defaultOptions() for a description of each
// value.
// @todo the block below is deprecated and as of Drupal 11 will be
// removed, query() will only return a StatementInterface object.
// @see https://www.drupal.org/project/drupal/issues/3256524
switch ($options['return'] ?? Database::RETURN_STATEMENT) {
case Database::RETURN_STATEMENT:
return $stmt;
// Database::RETURN_AFFECTED should not be used; enable row counting
// by passing the appropriate argument to the constructor instead.
// @see https://www.drupal.org/node/3186368
case Database::RETURN_AFFECTED:
$stmt->allowRowCount = TRUE;
return $stmt->rowCount();SQL insert
Certain databases require special handling for LOB (Large OBject, such as TEXT in MySQL) and BLOB (Binary Large OBject) fields, so a layer of abstraction is required to allow individual database drivers to implement whatever special handling they require.
Insert queries are started using the insert() method as follows:
/** @var \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection $connection */
$connection = \Drupal::service('database');
$query = $connection->insert('mytable', $options);That creates an insert query object that will insert one or more records to the mytable table. Note that braces are not required around the table name as the query builder will handle that automatically.
The insert query object uses a fluent API. That is, all methods (except execute()) return the query object itself, allowing method calls to be chained.
The insert query object supports a number of different usage patterns to support different needs. In general, the workflow consists of specifying the fields that the query will insert into, specifying the values the query will insert for those fields, and executing the query.
Here is an example in the compact form with chained together commands:
$result = $connection->insert('mytable')
->fields([
'title' => 'Example',
'uid' => 1,
'created' => \Drupal::time()->getRequestTime(),
])
->execute();which is equivalent to:
INSERT INTO {mytable} (title, uid, created) VALUES ('Example', 1, 1221717405);You can insert multiple rows using the multi-insert form of an insert query. This will execute three insert statements together as a single unit, using the most efficient method for the particular database driver in use. Note that here we have saved the query object to a variable so that we can loop on $values and call the values() method repeatedly
$values = [
['title' => 'Example 1', 'uid' => 1, 'created' => \Drupal::time()->getRequestTime()],
['title' => 'Example 2', 'uid' => 1, 'created' => \Drupal::time()->getRequestTime()],
['title' => 'Example 3', 'uid' => 1, 'created' => \Drupal::time()->getRequestTime()],
];
$query = $connection->insert('mytable')
->fields(['title', 'uid', 'created']);
foreach ($values as $record) {
$query->values($record);
}
$result = $query->execute();Note
What are the differences between insert() and query()?
insert()has each column specified as a separate entry in the fields array and the code can clean each column value.query()has anSQLstring with no way of checking individual columns.If you use
query()with placeholders, the code can check the column values but placeholders are just an option, there is no way to ensure yourSQLdoes not contain values not passed through placeholders.insert()passes the request through a set of hooks to let other modules check and modify your requests. This is the right way to work with other modules.query()is slightly faster because it does not pass the request through the hooks. You might save processing time but your code will not let other modules help your code.insert()is more likely to work with other databases and future versions of Drupal.
SQL Insert Query Example
/**
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function insert() {
/** @var \Drupal\Core\Database\Connection $connection */
$connection = \Drupal::service('database');
// single insert.
$result = $connection->insert('donors')
->fields([
'name' => 'Singleton',
'amount' => 1,
])
->execute();
// Note, there is an auto-increment field so insert() returns the value
// for the new row in $result.
$str = "Single insert returned auto-increment value of $result";
// Multi-insert1.
$result = $connection->insert('donors')
->fields(['name', 'amount',])
->values(['name' => 'Multiton1', 'amount' => 11,])
->values(['name' => 'Multiton1', 'amount' => 22,])
->execute();
$str .= "<br/>Multi-insert1 added 2 rows";
// Multi-insert2.
$values = [
['name' => 'Multiton1', 'amount' => 111,],
['name' => 'Multiton2', 'amount' => 222,],
['name' => 'Multiton3', 'amount' => 333,],
['name' => 'Multiton4', 'amount' => 444,],
['name' => 'Multiton5', 'amount' => 555,],
];
$query = $connection->insert('donors')
->fields(['name', 'amount',]);
foreach ($values as $record) {
$query->values($record);
}
$result = $query->execute();
$str .= "<br/>Multi-insert2 added 5 rows";
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}More at Insert Queries on drupal.org - updated Nov 2023
SQL Delete query
use Drupal\Core\Database\Database;
public function deleteQuery2() {
$database = \Drupal::database();
$query_string = "Delete FROM {donors} where id>10 ";
$affectedRows = $database->query($query_string,[],['return' => Database::RETURN_AFFECTED]);
$str = "Affected rows = $affectedRows";
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}Note
This will return the number of rows affected by the SQL delete query, although this RETURN_AFFECTED functionality will be deprecated in Drupal version 11. See rowCount for Drupal 9 and Drupal 10 source code.
// Depending on the type of query we may need to return a different value.
// See DatabaseConnection::defaultOptions() for a description of each
// value.
// @todo the block below is deprecated and as of Drupal 11 will be
// removed, query() will only return a StatementInterface object.
// @see https://www.drupal.org/project/drupal/issues/3256524
switch ($options['return'] ?? Database::RETURN_STATEMENT) {
case Database::RETURN_STATEMENT:
return $stmt;
// Database::RETURN_AFFECTED should not be used; enable row counting
// by passing the appropriate argument to the constructor instead.
// @see https://www.drupal.org/node/3186368
case Database::RETURN_AFFECTED:
$stmt->allowRowCount = TRUE;
return $stmt->rowCount();Paragraph static query example
In the txg.theme file this code digs into a table for a paragraph field and grabs the delta field value using a static query.
function txg_preprocess_paragraph__simple_card(&$variables) {
$card_parent = $variables['paragraph']->getParentEntity();
if ($card_parent->bundle() == 'home_aof_card') {
$variables['parent_delta'] = 0;
$database = Database::getConnection();
$result = $database->query("
Select delta from node__field_para_aofs n where n.bundle = 'home_page' AND n.field_para_aofs_target_id = :target_id", [':target_id' => $card_parent->id()]
);
if ($result) {
while ($row = $result->fetchAssoc()) {
$variables['parent_delta'] = $row['delta'];
}
}
$parent_label = $card_parent->field_ref_aof->entity->label();
$parent_path = $card_parent->field_ref_aof->entity->toUrl()->toString();
$variables['parent_label'] = $parent_label;
$variables['parent_path'] = $parent_path;
}
}Useful queries and snippets
Here are some useful little queries that you can paste into your SQL tools (e.g. SequelAce, SequelPro, PhpMyAdmin, etc.) or use directly in MySQL using the command line ddev drush sqlc:
ddev drush sqlc
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 134650
Server version: 5.7.42-0ubuntu0.18.04.1-log (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [db]> SELECT table_name, round(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) as SIZE_MB FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = DATABASE() ORDER BY SIZE_MB DESC LIMIT 10;List of top 10 biggest tables
SELECT table_name, round(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2)
as SIZE_MB
FROM information_schema.TABLES
WHERE table_schema = DATABASE()
ORDER BY SIZE_MB
DESC LIMIT 10;This outputs something like this:
+----------------------------------+---------+
| table_name | SIZE_MB |
+----------------------------------+---------+
| node_field_data | 499.25 |
| path_alias | 446.16 |
| search_api_db_default_index_text | 424.98 |
| node | 209.55 |
| cache_entity | 187.59 |
| search_api_db_default_index | 186.80 |
| node_field_revision | 164.80 |
| search_api_item | 152.67 |
| node_access | 146.98 |
| path_alias_revision | 126.14 |
+----------------------------------+---------+
10 rows in set (0.141 sec)More on Stack Overflow
Format output from a select query
The table format default output is hard to read. The G option will format the output in a more readable way.
Usual format from a select query:
MariaDB [db]> select * from sessions;
+-----+---------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| uid | sid | hostname | timestamp | session |
+-----+---------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 6_GYbpm8eu1MbvTyL9j-bh6d6fcPci-1aoNcVbp835o | 172.21.0.5 | 1741612580 | _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1741612556;s:1:"c";i:1741186093;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"fBirJVd_IQx5LXxF4WlzuLiR6hy0DUc2TcTQqRPaPJE";} |
| 1 | 7e-OPABLA2IXPqpqyrN3vH7RDwM6znr38TDZ0VZsB5Q | 172.23.0.1 | 1742318727 | _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1742318728;s:1:"c";i:1742318543;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"op5lgAFvLVolHUvhbpgkEDNYU4E-j-IiUq0y0qyLaiU";} |
| 1 | EKYp2HPCPG2zB_KKM4O-wRvm1C8AQ8yxT515NkhbjVs | 172.23.0.1 | 1742243572 | _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1742243573;s:1:"c";i:1741399093;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"m0l275rVN9rasGTpCNADkWC_ls0oD00hS6nXRpZOpuc";} |
| 1 | shKeFAj1njr0NVOhtsy-R8WXaDueWXE_NN_yqa0gIko | 172.21.0.5 | 1741185985 | _sf2_attributes|a:2:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";s:12:"pass_reset_1";s:74:"3v9Susa6Ge_XRS80_x_tHx-qYROShIBkBu0QsORMtbbs1qPtILqUFtCeZomEvWnz4mlS-ZEKcQ";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1741185985;s:1:"c";i:1741185985;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"JwJT4PItEyHJwxEJ_NC8Cxa4jzrYuoW6q-Kt8rlyjUI";} |
+-----+---------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
4 rows in set (0.009 sec)To format the output in a more readable way, use the G option. There is a backslash before the G to escape it.:
MariaDB [db]> select * from sessions\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
uid: 1
sid: 6_GYbpm8eu1MbvTyL9j-bh6d6fcPci-1aoNcVbp835o
hostname: 172.21.0.5
timestamp: 1741612580
session: _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1741612556;s:1:"c";i:1741186093;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"fBirJVd_IQx5LXxF4WlzuLiR6hy0DUc2TcTQqRPaPJE";}
*************************** 2. row ***************************
uid: 1
sid: 7e-OPABLA2IXPqpqyrN3vH7RDwM6znr38TDZ0VZsB5Q
hostname: 172.23.0.1
timestamp: 1742318727
session: _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1742318728;s:1:"c";i:1742318543;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"op5lgAFvLVolHUvhbpgkEDNYU4E-j-IiUq0y0qyLaiU";}
*************************** 3. row ***************************
uid: 1
sid: EKYp2HPCPG2zB_KKM4O-wRvm1C8AQ8yxT515NkhbjVs
hostname: 172.23.0.1
timestamp: 1742243572
session: _sf2_attributes|a:1:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1742243573;s:1:"c";i:1741399093;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"m0l275rVN9rasGTpCNADkWC_ls0oD00hS6nXRpZOpuc";}
*************************** 4. row ***************************
uid: 1
sid: shKeFAj1njr0NVOhtsy-R8WXaDueWXE_NN_yqa0gIko
hostname: 172.21.0.5
timestamp: 1741185985
session: _sf2_attributes|a:2:{s:3:"uid";s:1:"1";s:12:"pass_reset_1";s:74:"3v9Susa6Ge_XRS80_x_tHx-qYROShIBkBu0QsORMtbbs1qPtILqUFtCeZomEvWnz4mlS-ZEKcQ";}_sf2_meta|a:4:{s:1:"u";i:1741185985;s:1:"c";i:1741185985;s:1:"l";i:2000000;s:1:"s";s:43:"JwJT4PItEyHJwxEJ_NC8Cxa4jzrYuoW6q-Kt8rlyjUI";}
4 rows in set (0.003 sec)Show variables from my.cnf
You can use these commands to make sure your my.cnf variables are set correctly e.g. show variables like 'max_allowed_packet'; or show variables like 'max%';
mysql> show variables like 'key_buffer%';
+-----------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+-----------+
| key_buffer_size | 536870912 |
+-----------------+-----------+Display current database in use
If you want to figure out which database is being used in the current session, use the database() function:
MariaDB [db]> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| db |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.012 sec)Show all databases
MariaDB [db]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| db |
| information_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.015 sec)Show all tables
MariaDB [db]> show tables;+----------------------------------+
| Tables_in_db |
+----------------------------------+
| block_content |
| block_content__body |
| block_content_field_data |
| block_content_field_revision |
| block_content_revision |
| block_content_revision__body |
| cache_access_policy |
| cache_bootstrap |
| cache_config |
| cache_container |
| cache_data |
| cache_default |
| cache_discovery |
| cache_dynamic_page_cache |
| cache_entity |
| cache_menu |
| cache_page |
| cache_render |
| cache_toolbar |
| cachetags |
| comment |
| comment__comment_body |
| comment_entity_statistics |
| comment_field_data |
| config |
| config_export |
| config_import |
| file_managed |
| file_usage |
| flood |
| help_search_items |
| history |
| key_value |
| key_value_expire |
| menu_link_content |
| menu_link_content_data |
| menu_link_content_field_revision |
| menu_link_content_revision |
| menu_tree |
| node |
| node__body |
| node__comment |
| node__field_image |
| node__field_tags |
| node_access |
| node_field_data |
| node_field_revision |
| node_revision |
| node_revision__body |
| node_revision__comment |
| node_revision__field_image |
| node_revision__field_tags |
| path_alias |
| path_alias_revision |
| queue |
| router |
| search_dataset |
| search_index |
| search_total |
| semaphore |
| sequences |
| sessions |
| shortcut |
| shortcut_field_data |
| shortcut_set_users |
| taxonomy_index |
| taxonomy_term__parent |
| taxonomy_term_data |
| taxonomy_term_field_data |
| taxonomy_term_field_revision |
| taxonomy_term_revision |
| taxonomy_term_revision__parent |
| user__roles |
| user__user_picture |
| users |
| users_data |
| users_field_data |
| watchdog |
+----------------------------------+
78 rows in set (0.010 sec)Show process list
MariaDB [db]> show full processlist;
+------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+----------+-----------------------+----------+
| Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Progress |
+------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+----------+-----------------------+----------+
| 6557 | db | 172.23.0.2:35630 | db | Query | 0 | starting | show full processlist | 0.000 |
+------+------+------------------+------+---------+------+----------+-----------------------+----------+
1 row in set (0.008 sec)Quickly clear all tables
CLEAR ALL TABLES in A DB
---------------------------------------
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
SET @tables = NULL;
SET SESSION group_concat_max_len = 1000000;
SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(table_schema, '.', table_name) INTO @tables
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'wfm'; -- specify DB name here.
SET @tables = CONCAT('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS ', @tables);
PREPARE stmt FROM @tables;
EXECUTE stmt;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
show tables;Generate TRUNCATE statements for all cache tables
This will generate a list of TRUNCATE statements for all tables that start with cache_. You can then copy and paste the output into your SQL tool to clear all cache tables.
SELECT concat('TRUNCATE TABLE `', TABLE_NAME, '`;')
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_NAME LIKE 'cache%'Generate statements to convert character set and collation type for all tables
This will generate a list of ALTER TABLE statements for all tables (in database f) in the database. You can then copy and paste the output into your SQL tool to convert all tables to utf8mb4 character set and utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci collation type.
SELECT CONCAT('ALTER TABLE `', TABLE_NAME, '` CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;')
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = 'f';Use the database abstraction layer to avoid SQL injection attacks
It is bad practice to concatenate data directly into SQL queries.
// Bad practice - don't do it!.
\Database::getConnection()->query('SELECT foo FROM {table} t WHERE t.name = '. $_GET['user']);Good Practice:
Use proper argument substitution. The database layer works on top of PHP PDO, and uses an array of named placeholders:
\Database::getConnection()->query('SELECT foo FROM {table} t WHERE t.name = :name', [':name' => $_GET['user']]);For a variable number of arguments, use an array of arguments or use the select() method. See examples of each below:
$users = ['joe', 'poe', $_GET['user']];
\Database::getConnection()->query('SELECT f.bar FROM {foo} f WHERE f.bar IN (:users[])', [':users[]' => $users]);$users = ['joe', 'poe', $_GET['user']];
$result = \Database::getConnection()->select('foo', 'f')
->fields('f', ['bar'])
->condition('f.bar', $users)
->execute();When forming a LIKE query, make sure that you escape condition values to ensure they don't contain wildcard characters like `"%"``:
db_select('table', 't')
->condition('t.field', '%_' . db_like($user), 'LIKE')
->execute();Make sure that users cannot provide any operator to a query's condition. For example, this is unsafe:
db_select('table', 't')
->condition('t.field', $user, $user_input)
->execute();Instead, set a list of allowed operators and only allow users to use those.
db_query, db_select, and db_like were deprecated and removed from Drupal 9 - instead, you should use a database connection object and call the query, select, and escapeLike methods on it (the parameters are the same).
Viewing the MariaDB General Query Log
ddev mysql -u root -prootSet the file path for the general query log. The general query log is a feature in MySQL that logs all SQL queries received from clients, as well as information about client connections and disconnections.
SET global general_log = 1;
SET global log_output = 'file';
SET global general_log_file = '/home/selwyn/queries.txt';Log into the database container and tail the log file:
ddev ssh -s db
tail -f queries.txtTo turn off the general query log:
SET global general_log = 0;or use ddev restart to restart all the containers.
The queries.txt file will automatically be deleted when the container is restarted.
Thanks to Dries Buytaert's Effortless inspecting of Drupal database queries article for this useful tip.
Create a custom table for your module
If you need a custom database table (or two) for use in a custom module, you can use hook_schema in your module.install file. This will cause the table(s) to be created at module install time and removed at module uninstall time.
function nocs_connect_schema() {
$schema['nocs_connect'] = [
'description' => 'Stores data from event log used to import/update content to site.',
'fields' => [
'id' => [
'type' => 'int',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Primary Key: Unique ID of event log event.',
],
'uuid' => [
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 255,
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => "Unique ID for content created or updated.",
],
'nid' => [
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 255,
'not null' => FALSE,
'description' => "Unique ID for content created or updated.",
],
'event' => [
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 255,
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Type of event e.g. UPDATE or ADD.',
],
'created' => [
'type' => 'int',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Content creation date.',
],
'updated' => [
'type' => 'int',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Content update date.',
],
'type' => [
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 255,
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Type of content created or updated.',
],
'version' => [
'type' => 'int',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => 'Content version number.',
],
'status' => [
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 255,
'not null' => TRUE,
'default' => 'NEW',
'description' => 'Status of event log row - NEW, PROCESSING, COMPLETE, or ERROR.',
],
],
'primary key' => ['id'],
'indexes' => [
'uuid' => ['uuid'],
'event' => ['event'],
'type' => ['type'],
],
];
return $schema;
}Accessing a custom table
From the XMLSitemap module
This example from web/modules/contrib/xmlsitemap/src/XmlSitemapLinkStorage.php accesses the xmlsitemap table and runs a quick query to see if the status or access fields are being changed. If they are, it sets a flag to regenerate the sitemap. The addExpression('1') method is used to simplify the query, and the range(0, 1) method is used to limit the query to the first row. This code could definitely have been written more clearly but it does show how to run a query on a table.
public function checkChangedLinks(array $conditions = [], array $updates = [], $flag = FALSE) {
// If we are changing status or access, check for negative current values.
$conditions['status'] = (!empty($updates['status']) && empty($conditions['status'])) ? 0 : 1;
$conditions['access'] = (!empty($updates['access']) && empty($conditions['access'])) ? 0 : 1;
$query = $this->connection->select('xmlsitemap');
$query->addExpression('1');
foreach ($conditions as $field => $value) {
$operator = is_array($value) ? 'IN' : '=';
$query->condition($field, $value, $operator);
}
$query->range(0, 1);
$changed = $query->execute()->fetchField();
if ($changed && $flag) {
$this->state->set('xmlsitemap_regenerate_needed', TRUE);
}
return $changed;
}This code snippet from web/modules/contrib/xmlsitemap/src/XmlSitemapLinkStorage.php shows a query that uses queryRange():
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function checkChangedLink(array $link, array $original_link = NULL, $flag = FALSE) {
$changed = FALSE;
if ($original_link === NULL) {
// Load only the fields necessary for data to be changed in the sitemap.
$original_link = $this->connection->queryRange("SELECT loc, access, status, lastmod, priority, changefreq, changecount, language FROM {xmlsitemap} WHERE type = :type AND id = :id", 0, 1, [':type' => $link['type'], ':id' => $link['id']])->fetchAssoc();
}
...The following snippet shows an example of using the merge command. This will add or update an existing link into the xmlsitemap table. In the web/modules/contrib/xmlsitemap/src/XmlSitemapLinkStorage.php file, the following code is used to write to the xmlsitemap table. Browse the source code here.
$queryStatus = $this->connection->merge('xmlsitemap')
->keys([
'type' => $link['type'],
'id' => $link['id'],
'language' => $link['language'],
])
->fields([
'loc' => $link['loc'],
'subtype' => $link['subtype'],
'access' => (int) $link['access'],
'status' => (int) $link['status'],
'status_override' => $link['status_override'],
'lastmod' => $link['lastmod'],
'priority' => $link['priority'],
'priority_override' => $link['priority_override'],
'changefreq' => $link['changefreq'],
'changecount' => $link['changecount'],
])
->execute();You can browse the source for the entire module here.
Debugging queries (and view the actual SQL)
Use the __toString() member to see what is really happening in a query. You can use the Evaluate dialog in PhpStorm to dynamically display the SQL query by typing in the query variable and ->__toString(). See the screenshot below for the output.
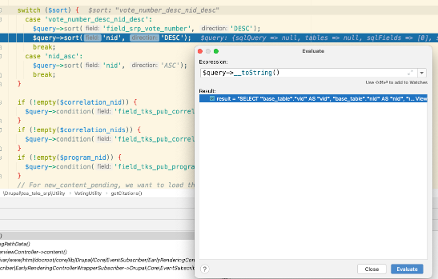
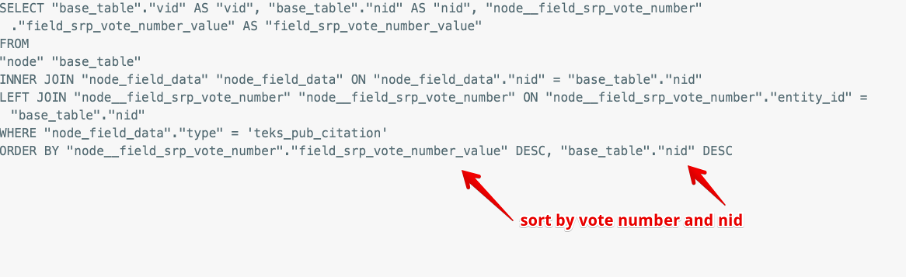
Click the teensy little View link on the right side of the evaluate dialog for this display:

I was able to tell what the sort criteria were:
Useful my.cnf settings
To enable error log add following
[mysqld]
log_error=/var/log/mysql/mysql_error.log
# To enable general query log add following
general_log_file = /var/log/mysql/mysql.log
general_log = 1
# To enable Slow Query Log add following
log_slow_queries = /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
long_query_time = 2
log-queries-not-using-indexesEnable logs at runtime
To enable logs at runtime, login to MySQL client (mysql -u root -p) and give:
SET GLOBAL general_log = 'ON';
SET GLOBAL slow_query_log = 'ON';Troubleshooting
Definer error
When loading a database and there are references in it to DEFINER= you might see this error
ERROR 1227 (42000) at line 7746: Access denied; you need (at least one of) the SUPER privilege(s) for this operationTo fix this, remove any reference to DEFINER=
e.g.
/*!50017 DEFINER="ruttnzsrnv"@"%"*/remove everything between the /* */ and try again
more at Stack Overflow
Unknown collation
When importing a db from and you see this error:
$ ddev import-db --src=dbprod.sql.gz
ERROR 1273 (HY000) at line 25: Unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci'
184KiB 0:00:00 [4.31MiB/s] [> ] 0%
ERROR: 1
Failed to import database db for dir: exit status 1From https://github.com/ddev/ddev/issues/1902:
More at Accent insensitivity and case insensitivity, two excellent things to have in collation
The workaround is to replace the ai_ci encoding part in the file with this sed command:
sed -i '' 's/utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci/utf8mb4_unicode_ci/g' 2019-10-26-prod.sqlthis may also work
Here is an oldish message from Randy Fay: I hope it's clear to everybody that in current versions of ddev, the fix is to use the MySQL database instead of mariadb. Use the mysql_version that matches your production server.
There's no need for a workaround in ddev. Please use the MySQL version that matches your server.
- ddev stop --remove-data
- Edit your .ddev/config.yaml to remove any mariadb_version. Add mysql_version: 5.7 or mysql_version: 8.0 or whatever matches your server version.
- ddev start
- ddev import-db --src=/path/to/your/sqldump.sql.gz
Again... if your server is using MySQL 8, please just change your ddev project to use MySQL 8.
ddev config --mariadb-version="" --mysql-version=8.0