Artificial Intelligence
Overview
This chapter is a little different from most of the others in the book. It is more about my exploration of the current state of AI for Drupal. Hopefully, it will grow as I (and others) use AI in Drupal more.
Cost
You can currently use the amazee.ai provider for free. If you want to use OpenAI, you have to preload your account with some money. This wasn't obvious to me.
You can confirm that this is working by navigating to the OpenAI playground and putting in some sort of a prompt. If you have successfully paid your account, you will see a response. Monitor your usage here.
AI Providers
There is a range of (ever-changing) AI providers available which can be used to provide AI services to your Drupal site. These include: OpenAI, Anthropic, Groq, OpenAI, Ollama, Huggingface, Imstudio, Mistral, Auphonic, AWS Bedrock, Deepgram, DeepL Translate, ElevenLabs, Fireworks AI, Google Gemini and amazee.ai.
amazee.ai
amazee.ai is a private AI infrastructure provider by amazee.io. It is designed with a strong focus on data sovereignty and privacy, allowing enterprises to keep sensitive data in their region and comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR.
Setting up amazee.ai is straightforward, requiring only a valid email. There is no need to manually generate and handle API keys between the provider and the Drupal module.
Drupal AI modules
AI module
The AI module - documentation here is the main player in this space. This module has so many interesting submodules which add all kinds of features. Think of it as a Swiss Army knife for AI in Drupal. This module is very much still in development, so expect to use the 1.0.x-dev version
AI Providers: Anthropic, Groq, OpenAI, Ollama, Huggingface, Imstudio and Mistral included in the module. You can also add Auphonic, AWS Bedrock, Deepgram, DeepL Translate, ElevenLabs, Fireworks AI and Google Gemini from their respective modules.
AI Explorer:- This is an area in the admin where you can explore text generation capability and ask it (prompt) whatever you like. An ideal place to test your prompts.
AI Search (Experimental):- Search through your content intelligently where the search understands the meaning of your terms with Semantic Search or ask a LLM Chatbot to explore your content, find it or answer questions about it. By integrating embeddings and vector databases into Search API we can reduce hallucinations in your LLMs or provide it access to more of your own data in what is known as “Retrieval Augmented Generation or RAG”. Currently support Milvus, Zilliz, and Pinecone.
Milvus VBD Provider(Experimental):- This module provides a vector database provider for the AI module. It uses the Milvus database to store and search vectors. The instructions for installing Milvus are here.
Note
The way to get to try out most of these features is to use the AI API Explorers at https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/ai/explorers.
Vertex AI Search
The Vertex AI Search module provides search capabilities using the Vertex AI Search
This module uses a Google back-end for indexing and allowing searching of your content using AI. This is a paid service, with pricing information here. This offers some pretty impressive features, including the ability to search for images based on their content. Try this query on the Mercari site to see this in action.
Local LLM engine
The Ollama locally run LLM for mac/win/linux/docker is available in a GitHub repo to install and run locally. This is a great way to test your prompts without incurring costs. The Ollama module is also available to use locally in Drupal.
AI Content Generators
I had great hopes for prompting the AI to create 50 blog posts for me, but sadly, that isn't the state of the content creation modules as of 11-7-2024.
AI Content Creator
This AI Content Creator module, unfortunately, requires a legacy OpenAI key and sadly has hard-coded an old model. When I change the code to use a more modern model, it does work. Also, it uses OpenAI only so none of the other providers are available. Also, it essentially provides the same functionality as the normal ChatGPT web interface, so it isn't as useful as I had hoped. It does serve as a useful example of how to interface with OpenAI from Drupal.
These are the code changes I had to make to get it working. I commented out the old stuff and put in the new below. From web/modules/contrib/ai_content_creator/ai_content_creator.module:
function ai_content_creator_generate_content_callback(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$values = $form_state->getUserInput();
$keywords = trim(preg_replace('/\s\s+/', ' ', $values['keywords']));
$ajax_response = new AjaxResponse();
$access_token = \Drupal::config('ai_content_creator.adminsettings')->get('api_key');
$url = \Drupal::config('ai_content_creator.adminsettings')->get('api_url');
$max_token = \Drupal::config('ai_content_creator.adminsettings')->get('api_max_token');
$payload = [
// "model" => "text-davinci-003",
"model" => "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125",
// "prompt" => $keywords,
"messages" => [
[
"role" => "user",
"content" => $keywords,
],
],
"temperature" => 0.9,
"max_tokens" => (int) $max_token,
];
...
// at the end of the same function:
//$text = (string) $data['choices'][0]['text'];
$text = (string) $data['choices'][0]['message']['content'];
$dialog_options['buttons']['clipboard']['data-clipboard-text'] = $text;
$ajax_response->addCommand(new OpenModalDialogCommand(t('AI generated content.'), nl2br($text), $dialog_options));
return $ajax_response;
}Content AI
The Content AI module is also tied to OpenAI. Unfortunately, this module's instructions are so confusing that I decided to rather explore the ai module and see if the Experimental AI Automators submodule can do what I want to generate sensible-looking content.
Implementing RAG
For more info on RAG, see the definition of the RAG term below.
Note
These instructions apply to using the Milvus VDB Provider which is also referred to as the Milvus/Zilliz VDB Provider in the extend listing in Drupal. You can apply most of these instructions to using a local setup of the Pinecone provider as well. Watch Scott Euser's video presentation for more details.
Following the instructions from the AI module docs
Copy the ddev-example.docker-compose.milvus.yaml to your .ddev folder with:
cp web/modules/contrib/ai/vdb_providers/vdb_provider_milvus/docs/docker-compose-examples/ddev-example.docker-compose.milvus.yaml .ddev/docker-compose.milvus.yamlAfter copying the docker-compose file to the .ddev folder and restarting ddev, you can see the Milvus UI at https://ddev103.ddev.site:8521. Note, my site is called ddev103 so you will need to change this to your site name.
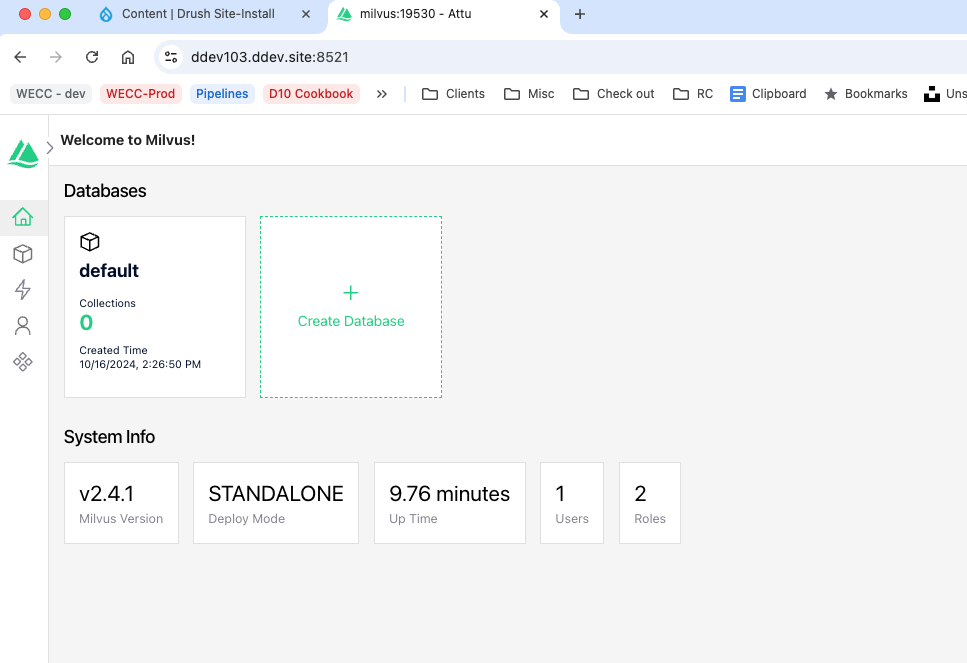
At this page, create a database. I created db1. You don't need to manually create a collection. This will be done for you later.
At https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/ai/vdb_providers/milvus use the following settings:`
Set up your Milvus Vector Database Plugin configuration to use:
Host: http://milvus
Port: 19530
API Key: Ignore this for a local Milvus instance.Setup the Search API to access Milvus
Add a server
At https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/search/search-api/add-server add a server. I called mine milvus, used the host milvus and port 19530. The database is the one (db1) that you created earlier in Milvus. For Vector Database configuration, I specified the following:
Database name: db1
Collection: collection1
Similarity Metric: Cosine similarityThe rest of the options are quite confusing and appear to be important. For more details, watch Scott Euser's video presentation. He explains how the content is broken into chunks and indexed into the vector database. Also, note that these chunks are submitted to the VDB along with contextual data like the creation date, content type, and title to help the AI understand the context of the content. This helps the AI to provide relevant search results.
Configure AI Search backend:
Embeddings engine: OpenAI | text-embedding-3-small
Tokenizer chat counting model: OpenAI - text-embedding-3-small
Vector Database: Milvus DBAdvanced Embeddings Engine Configuration:
Set Dimensions Manually: unchecked
Number of dimensions: 1536Advanced Embeddings Strategy Configuration:
Strategy for breaking content into smaller chunks for indexing: Enriched Embedding Strategy
Maximum chunk size allowed when breaking up larger content: 500 max_tokens
Minimum chunk overlap for main content: 100 max_tokens
contextual content maximum percentage: 30%Add search index
Following a similar practice for normal setup of an index for the search API, add an index at https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/search/search-api/add-index. I called mine content and specified all content types. Watch out on that screen for the confusing content type selection options. Also, be sure to set the cron batch size to 5. It defaults to 50 which is too high for Milvus. It takes a long time to index content.
The options look like:
Datasources: Content
indexing order: Index items in the same order they were saved
Server: Milvus
enabled: check
Index items immmediately: check
Track changes in referenced entities: check
Cron batch size: 5Add fields to index
at https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/search/search-api/index/content/fields add the following fields:
- Rendered HTML output (rendered_item)
- Authored on (created)
- Content type (type)
- Published (status)
- Title (title)
For the rendered_item field, use the following settings:
User roles: anonymous user
view mode for Content >> Article: Search index
View mode for Content >> Basic page: Search indexThis will vary for your content types. The search index view mode is already set up by the Search API module so it is a good choice. The remainder of the fields won't have any settings to change.
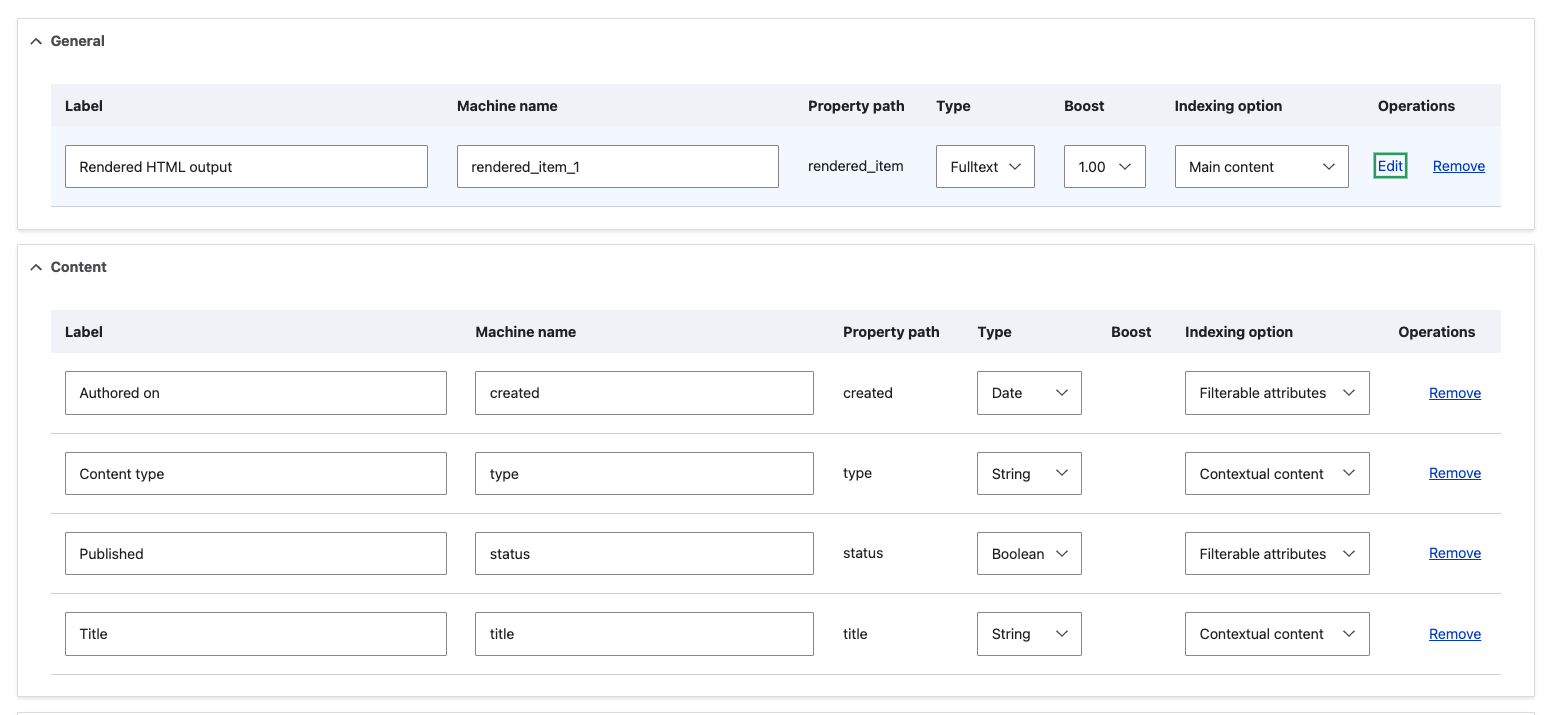
Back on the Manage fields for search index Content page, you will need to configure the Vector Database indexing options. This is really important.
In the General section, add the Rendered HTML output field as fulltext type, with a boost of 1.00 and specify the indexing option as Main content.
In the Content section, set the Authored on and Published fields as filterable attributes. This is similar to allowing faceted search. For the Content type and Title fields, specify them as contextual content so that the AI can understand the context of the content.
See the screenshot below for what it should look like:
It would be useful to also add an abstract or summary to the indexed field and specify it as Contextual content to further help the AI understand the context of the content.
Check your work
You need to make sure the content will be submitted to the VDB correctly. To test this, you can use the Preview content to be vectorized section at https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/search/search-api/index/content/fields.
Type in part of a title for your content. I used green bean and it found the Green Bean Bonanza: 3 delicious dishes to savor node. After clicking the node title, it showed the node had been broken up into 4 chunks (ID 8:en0, 8:en1, 8:en2, 8:en3) and each chunk was displayed along with the contextual fields:
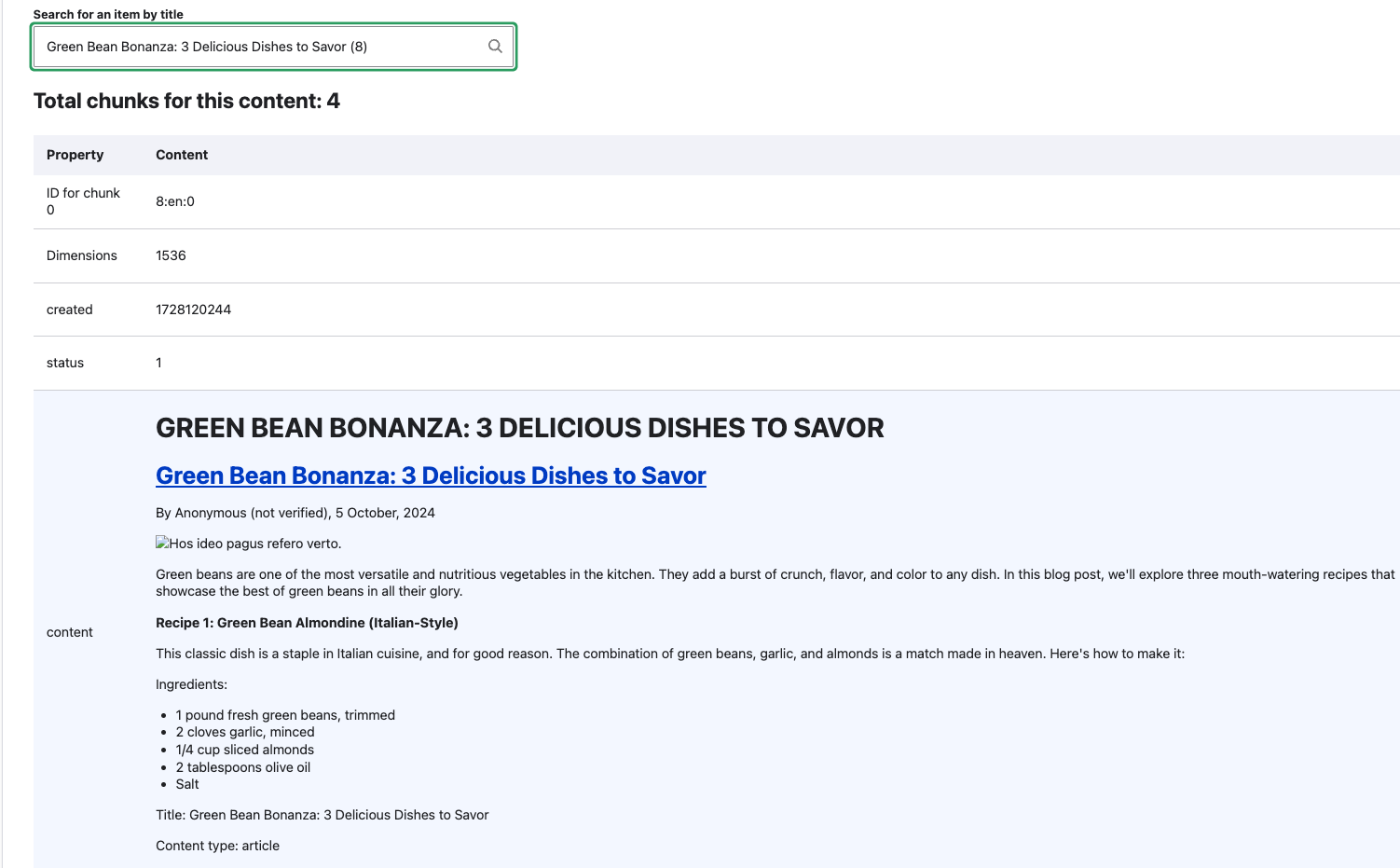
And here is the 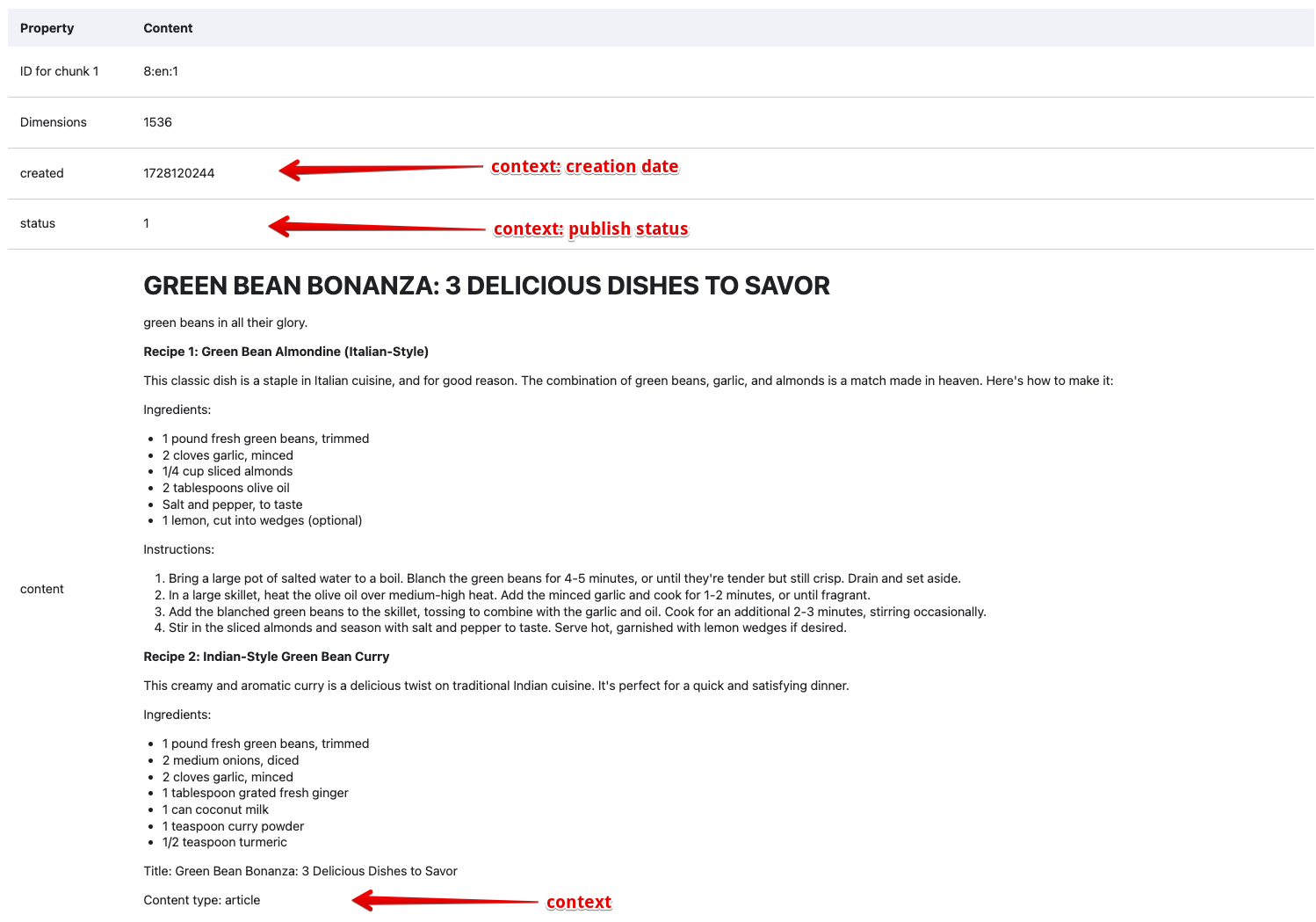
At https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/search/search-api/index/content, use the u/i to index the content. You will need to have some content to index. I used ChatGPT to generate some articles so I had 8 nodes to index. Afterwards, the index status should show 100% and in my case 8/8 indexed.
In the browser, navigate to https://ddev103.ddev.site:8521/ as before, click on the db1 database. You should see a list of collections. Check the Approx Count column to see if your content has been indexed. It needs to be greater than zero:
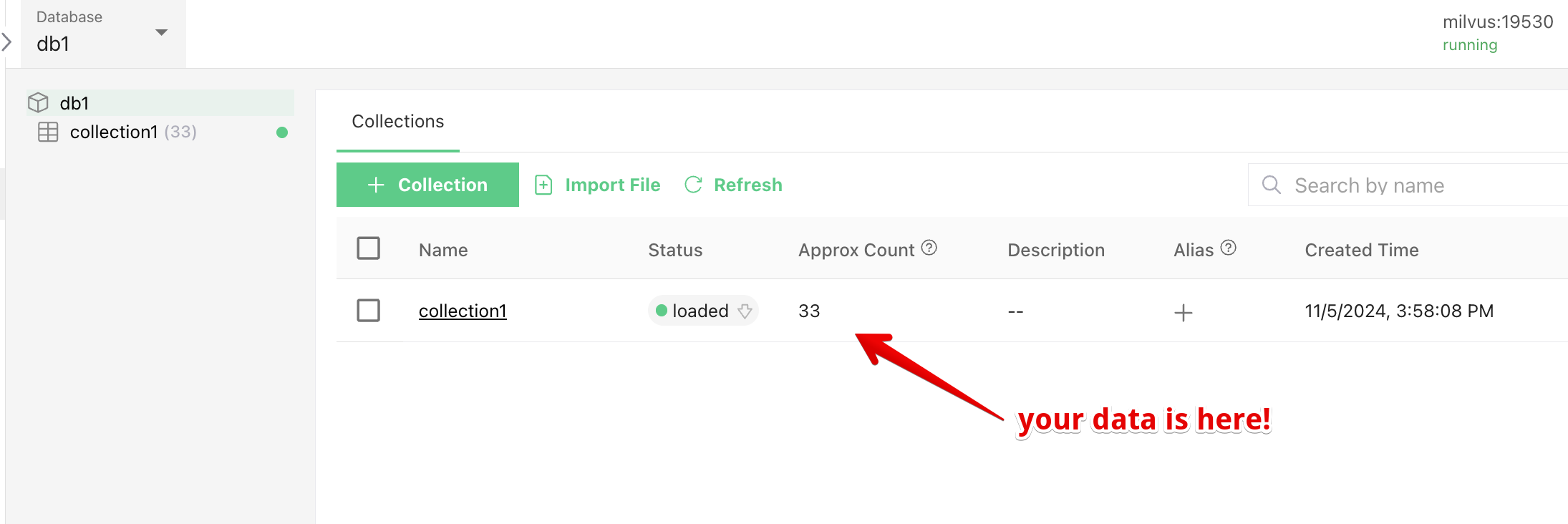
Altering the query to Boost AI results
This is a technique to modify the search query to customize the results. This is required for RAG so that the AI results are boosted in the search results to appear first.
I've seen this technique used to boost results in other cases, e.g. to make the results which are type staff appear earlier in the results set. See an example and explanation in the general section
In the AI module in web/modules/contrib/ai/modules/ai_search/src/Plugin/search_api/processor/SolrBoostByAiSearch.php, the description explains that AI Search results will be inserted into the database search results:
/**
* Prepend AI Search results into the database search..
*
* @SearchApiProcessor(
* id = "solr_boost_by_ai_search",
* label = @Translation("Boost SOLR by AI Search"),
* description = @Translation("Prepend results from the AI Search into the SOLR results ready for subsequent filtering (if any) to improve relevance."),
* stages = {
* "preprocess_query" = 0,
* }
* )
*/The preprocessSearchQuery() method is responsible for modifying the search query before it is executed. It checks if there are search terms and, if so, retrieves AI search results. These results are then added as tags to the query to be processed below.
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function preprocessSearchQuery(QueryInterface $query) {
parent::preprocessSearchQuery($query);
// Only do something if we have search terms. It is possible that the
// index is being filtered only without any terms, in which case we have
// nothing more to do.
if ($query_string_keys = $query->getKeys()) {
$ai_results = $this->getAiSearchResults($query_string_keys);
if ($ai_results) {
// This gets passed via the SolrBoostByAiSearchEventSubscriber class
// back to the queryAlter() method.
$query->setOption('ai_search_ids', $ai_results);
}
}
}Later, in web/modules/contrib/ai/modules/ai_search/src/EventSubscriber/SolrBoostByAiSearchEventSubscriber.php, in the onPostConvertedQuery() method, an event is fired to alter the query is altered and boost the AI results:
/**
* Alters the Solarium query to boost AI results.
*
* @param \Drupal\ai_search\Event\PostConvertedQueryEvent $event
* The event containing the Solarium query.
*/
public function onPostConvertedQuery(PostConvertedQueryEvent $event) {
$solarium_query = $event->getSolariumQuery();
$query = $event->getSearchApiQuery();
SolrBoostByAiSearch::queryAlter($solarium_query, $query);
}Here is the queryAlter() method in the web/modules/contrib/ai/modules/ai_search/src/Plugin/search_api/processor/SolrBoostByAiSearch.php class that is called from the code above. The queryAlter() static method alters the database query by extracting entity IDs from the query tags and modifies the query to boost the AI result entity IDs. It adds an expression to the query to prioritize these IDs and adjusts the order by clause to ensure AI results appear first.:
/**
* Alter the SOLR Query to elevate specific IDs.
*
* @param \Solarium\Core\Query\QueryInterface $solarium_query
* The SOLR query.
* @param \Drupal\search_api\Query\QueryInterface $query
* The Search API query.
*/
public static function queryAlter(SolariumQueryInterface $solarium_query, QueryInterface $query): void {
$ai_search_ids = $query->getOption('ai_search_ids');
if (empty($ai_search_ids)) {
return;
}
// The item IDs are stored with a prefix that includes the server and index
// ID, followed by the item ID.
$index = $query->getIndex();
$hash = $index->getServerInstance()->getBackend()->getTargetedSiteHash($index);
$prefix = $hash . '-' . $index->id() . '-';
// Build the parameter string and set to elevate these IDs.
// The elevate IDs option respects the order provided, so the results
// will therefore respect the order provided by the AI Search relevance.
$param_parts = [];
foreach (array_keys($ai_search_ids) as $ai_search_id) {
$param_parts[] = $prefix . $ai_search_id;
}
$solarium_query->addParam('elevateIds', implode(',', $param_parts));
}There is also code which uses the now deprecated hook_search_api_solr_query_alter() to alter the query in web/modules/contrib/ai/modules/ai_search/ai_search.module and web/modules/contrib/ai/modules/ai_search/src/Plugin/search_api/processor/DatabaseBoostByAiSearch.php. Sadly, this means it won't work for Drupal 10. I suspect it will be removed. It needs to be converted to use the event subscriber as described in How to replace the deprecated hook hook_search_api_solr_query_alter with PreQueryEvent on drupal.org - updated Apr 2024. It is interesting and perhaps useful to look at.
The preprocessSearchQuery method in the DatabaseBoostByAiSearch class is responsible for modifying the search query to include AI-boosted results. It first checks if there are search terms in the query. If search terms exist, it retrieves AI search results using these terms. If AI results are found, it adds specific tags to the query, including database_boost_by_ai_search and ai_search_ids with the IDs of the AI-boosted entities. This tagging is used later to alter the database query to prioritize these AI-boosted results.
Searching
To actually do the searching, you have to use the AI Vector DB Explorer. I found this at https://ddev103.ddev.site/admin/config/ai/explorers/vector-db-search.
I tested by providing the prompt: are there any green bean-related products referenced in the posts? and it responded with some results that showed recipes that included green beanin the title. The same search where I used the French word for green beans:are there any haricot verts related products referenced in the posts?gave me results with green beans in the title and recipes. The AI doesn't seem to care what language, it apparently has indexed theideaof green beans and can find it regardless of the language. This is pretty impressive. I even tried it usingare there judías verdes referenced in the posts?` which is the Spanish version and it worked great!
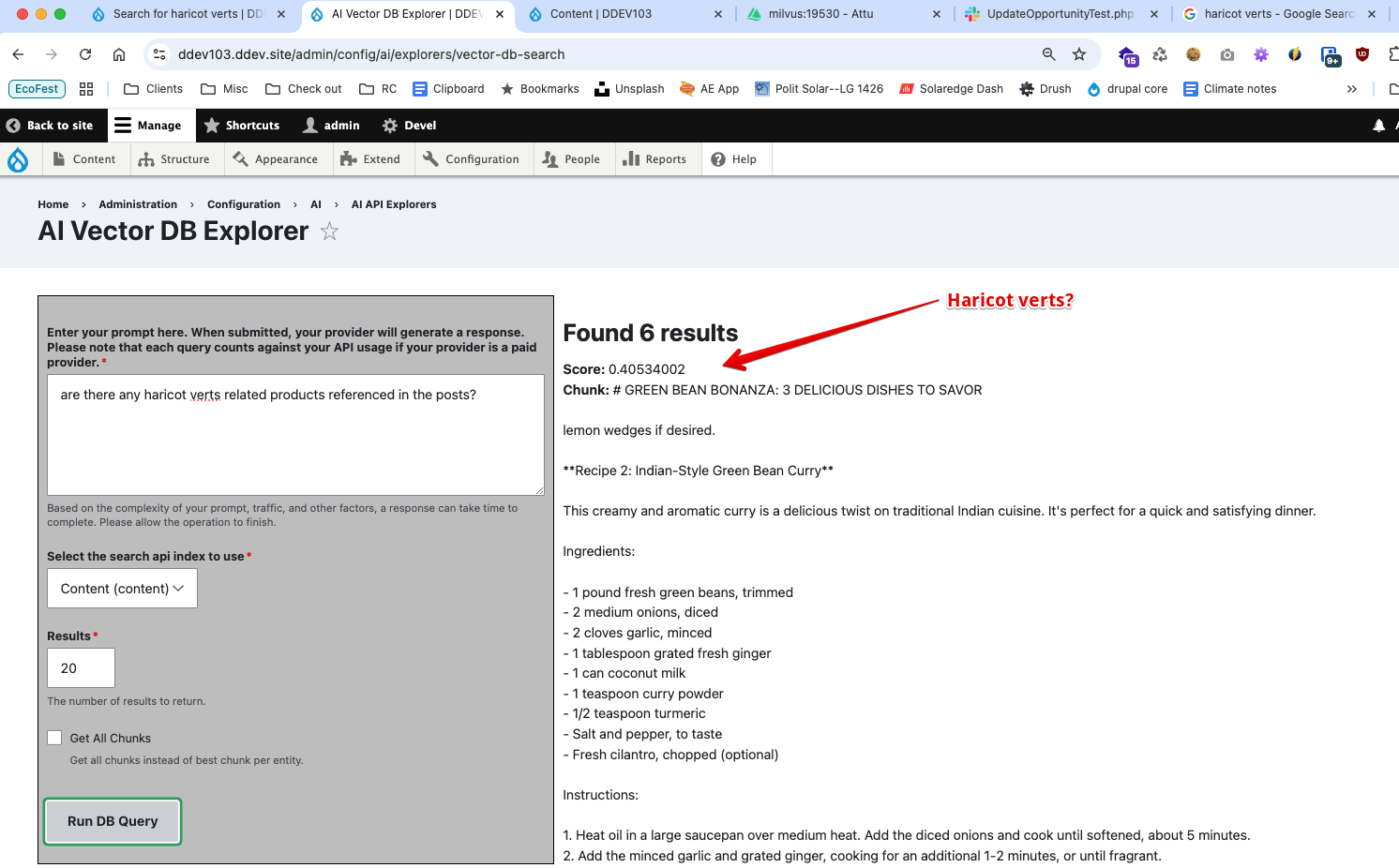
A simple site search at https://ddev103.ddev.site/search/node?keys=haricot verts for the French term haricot verts returned no results. This is a good example of how the AI search is superior to the normal search. AI search is able to understand the context of the content and provide relevant results, whereas the normal search is just looking for the exact term in the content.
In some of my earlier exploration, when I put in a prompt, I got an error that Method embeddings does not exist on provider groq. I think the problem was that I had configured the groq provider to handle the embeddings which it doesn't do. When I later changed it to use the OpenAI provider, it worked fine.
API keys
Each service requires an API key. The OpenAI key is a little more challenging than most as they have legacy keys which are used by some modules, e.g., AI Content Generator.
OpenAI
Start at the Usage page and select API keys on the left side. Follow the instructions on this page for the new Project API keys. If you need a legacy key, click on the view user API keys button on the right. Here you can create the new keys.
Terms
RAG
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation, which is an AI framework that combines the capabilities of generative large language models (LLMs) with traditional information retrieval systems.
From this nvidia blog post from Nov 2023: Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a technique for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of generative AI models with facts fetched from external sources.
In other words, it fills a gap in how LLMs work. Under the hood, LLMs are neural networks, typically measured by how many parameters they contain. An LLM’s parameters essentially represent the general patterns of how humans use words to form sentences.
I did some testing by asking questions of my site, such as: Is there anything about floating around in the ocean on fiberglass boards? and it showed me articles about surfing. I could also reference words in other languages which the AI could easily translate and find the relevant content.
Vector Database
A vector database (VDB) is a type of database that stores data as mathematical representations, or vectors, to manage and search for unstructured and semi-structured data. It keeps track of the relationships between data points, including their similarities.
Vector databases make it easier for machine learning models to remember previous inputs, allowing machine learning to be used to power search, recommendations, and text generation use-cases. Data can be identified based on similarity metrics instead of exact matches, making it possible for a computer model to understand data contextually. More at this Cloudflare article
Examples of vector database products. Some can be hosted locally or are offered as a service:
TODO
- check out Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG) module
- check out Build Smart Drupal Chatbots with RAG Integration and Ollama by Akansha Saxena Jul 2024
- check out Using RAG to Talk to Drupal Site Content. This looks like the blueprint for Akansha's article.
- check out this Apply RAG, OpenAI integrations and interpolation - Frederik Wouters video - Audio is very bad..
Resources
- Drupal Slack #ai channel
- Drupal AI Online Meetup #2. This contains the link to the YouTube presentation by Scott Euser (Soapbox).
- How to Set Up the OpenAI Module in Drupal 10 - Jan 2025
